Joint and muscle disorders
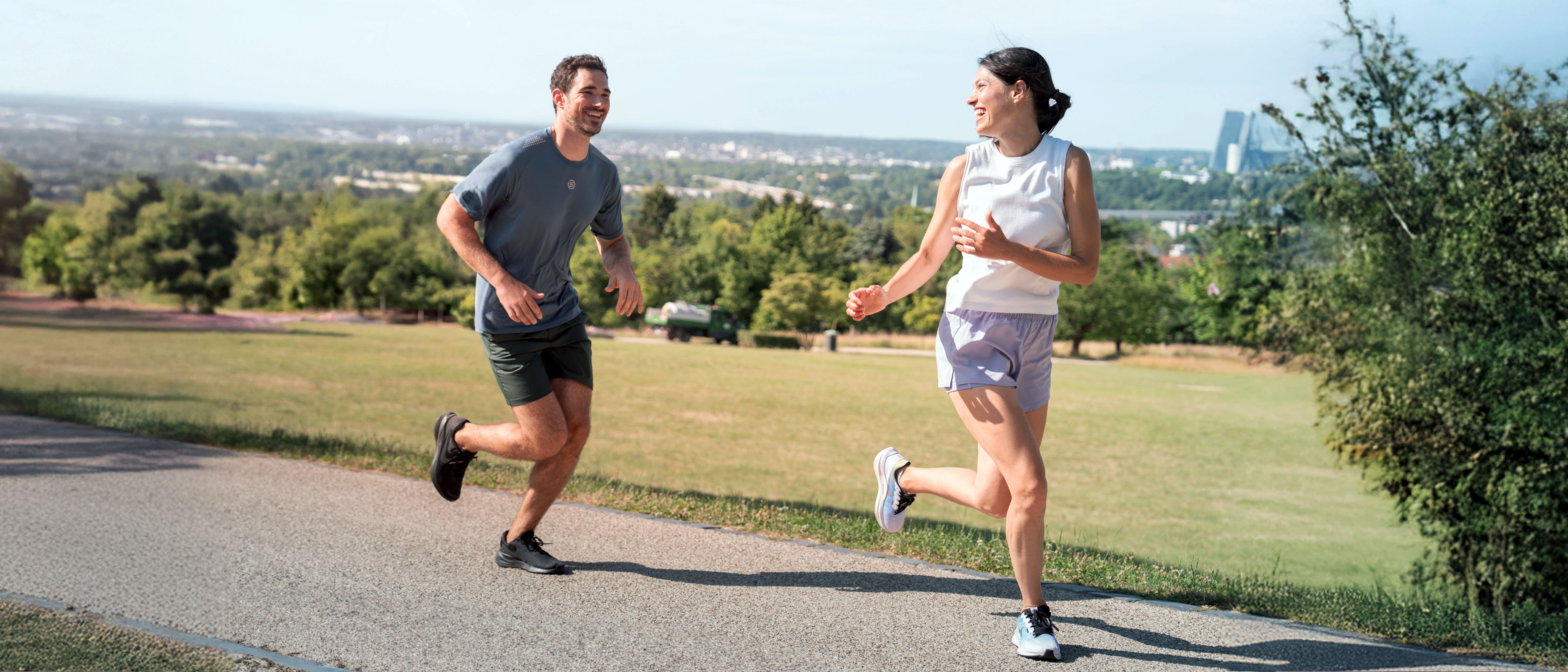
We rely on our muscles, joints, and tendons in daily life and for sports activities. Yet sometimes, it's only after an awkward move or overload that we fully appreciate their function. But how do sore muscles and other injuries actually happen? And even more importantly, how can we avoid injury happening?
What are the symptoms of musculoskeletal disorders?
Exercise keeps our body healthy and fit. But as with most things, the correct amount matters. Too much sitting can harm our musculoskeletal system, just as much as excessive training. A wrong step, a moment of inattention or excessive ambition can represent a danger to muscles, joints, and tendons.
Disorders during sports
We know from our own experience how unpleasant muscle soreness can be. If these conditions are acute or recurrent, they are still a comparatively harmless problem.
Various team sports such as soccer or handball have their own risk potential. The same is true of sports that involve explosive movements, such as tennis, squash, or badminton. Sports with uniform movement patterns, such as cycling, inline skating, or jogging can also easily lead to overload.
Despite this, the solution is not to avoid sports, because an active lifestyle is the most important precondition for avoiding musculoskeletal disorders.


Disorders in everyday life
Whether commuting, in the office, or on the sofa in the evening, many people spend most of their day seated. If this is not balanced by active leisure time, back problems are inevitable. Yet even when gardening or doing home improvement, our musculoskeletal system can be affected. A stooped position, kneeling for long periods or incorrect lifting can frequently involve tension and can result in injury.
What are the causes of joint, muscle, and tendon disorders?
There are various causes of musculoskeletal disorders. They are generally divided into two categories. If disorders occur without an external influence, they are referred to as endogenous causes. By contrast, exogenous causes can be attributed to external influences.
Examples of endogenous causes are
- Improper training technique
- Insufficient regeneration
- Inadequate warm-up or stretching
- Overload
- Poor posture
Examples of exogenous causes are
- Injury by a sports opponent
- Inadequate training equipment or improper footwear
- Inappropriate flooring or surface
- Poor weather conditions
What can be done about musculoskeletal disorders?
First, the good news: Our body has an enormous ability to regenerate muscles, joints, and tendons itself. In order for this natural process to proceed as smoothly as possible, it is necessary to react quickly in the event of disorders. The body can also be given targeted support during regeneration; disorders can be prevented by a well coordinated response.
Take the right approach in acute cases
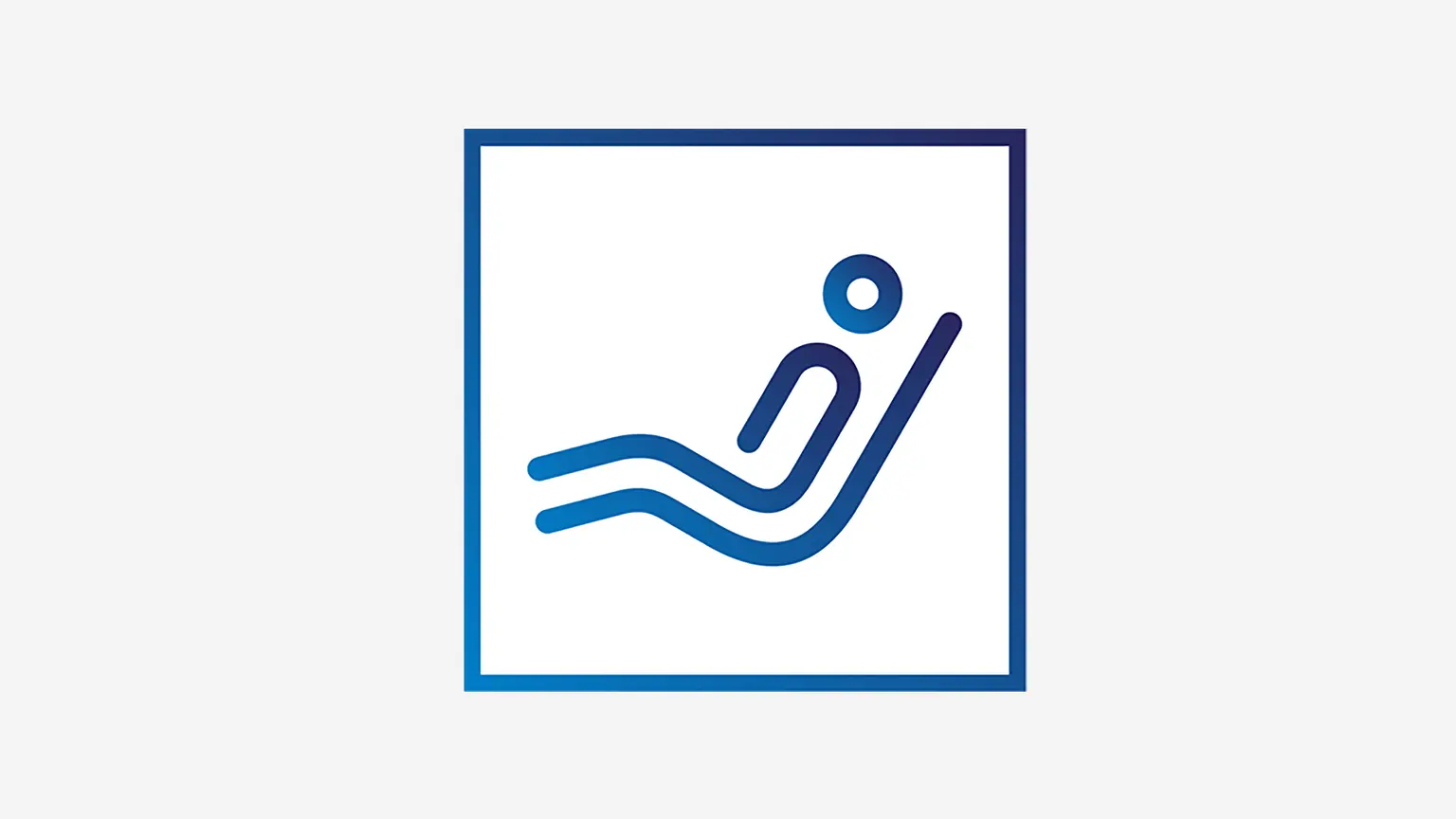
Following the so-called RICE rules has proven successful for acute muscle and joint disorders.
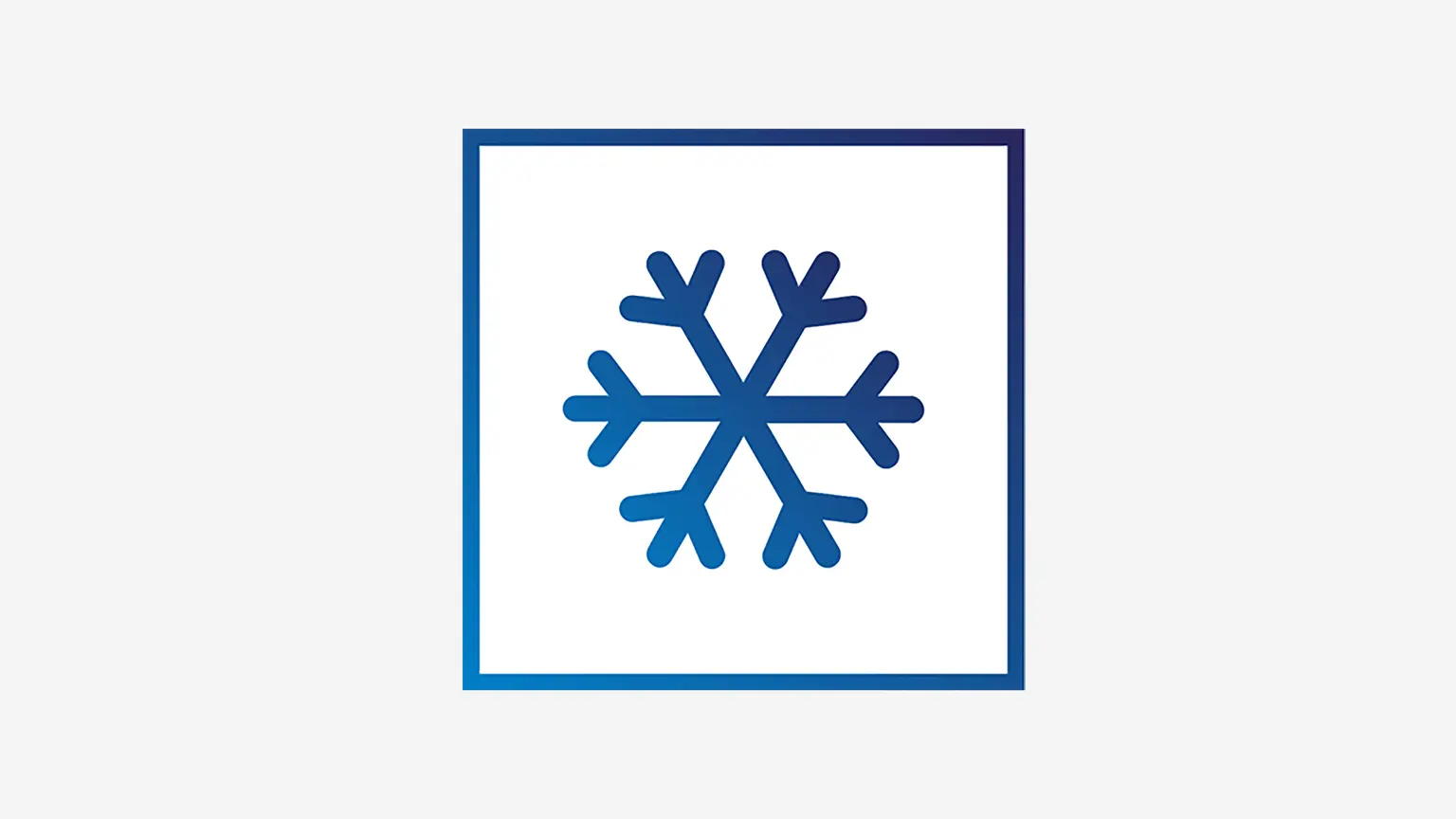
Cooling or heating? It depends!
Cooling the affected body part is advisable for acute disorders. By contrast, heat can help in cases of tension or frequently recurring disorders.
A healthy diet is the basis for regeneration
A diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids can help keep inflammatory processes in-check. Particularly high amounts of omega-3 are found in flax seeds and fatty fish, such as salmon. In addition, to prevent muscle deterioration, it's important to eat sufficient protein.
Natural companions for everyday life and sports
In addition to a healthy and balanced diet, there are other options for supporting the body naturally during regeneration. For example, topical medication with natural ingredients, such as Traumeel®, are available for this purpose.
When should I seek medical attention?
Discomfort or disorders that last for several days or longer should always be checked by a general physician. They will generally examine the affected body region through palpation or imaging methods such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), in order to rule out serious injury.
Depending on the diagnosis, support by a physiotherapist can be useful. They can help correct poor posture and provide training in healthy movement patterns. Physiotherapy can also help relieve discomfort and prevent future problems.
Exercise is the best prevention
To properly recover, the body needs adequate time and rest. Musculoskeletal disorders call for a slow and careful return to fitness activity. Repeat problems can be prevented by specialized training of muscles in the trunk, arms, and legs in a targeted manner. This provides stabilization for joints and relief for tendons and ligaments.
In addition, regardless of the type of sport, a thorough warm-up is advisable to bring the body to a working temperature and prepare the musculoskeletal system for the upcoming stress. If joint discomfort or disorders frequently recur, activities that are gentle on the joints, such as yoga, Pilates, or swimming, are recommended.
Avoid H.A.R.M.
Heel natural medicines
Lymphomyosot® in your country
Please choose your country. You will leave this website and will be redirected to your local website to get more information about Lymphomyosot®.
Zeel® in your country
Please choose your country. You will leave this website and will be redirected to your local website to get more information about Zeel®.
Spascupreel® in your country
Please choose your country. You will leave this website and will be redirected to your local website to get more information about Spascupreel®.